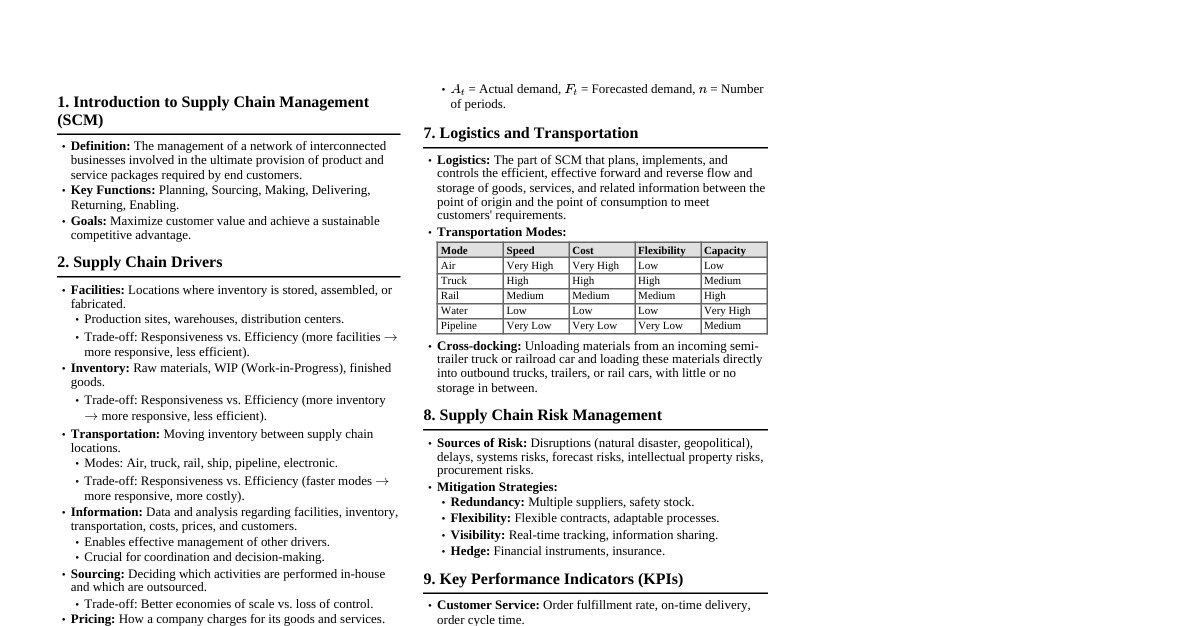
1. Introduction to Supply Chain Management (SCM) Definition: SCM is the management of a network of interconnected businesses involved in the ultimate provision of product and service packages required by end customers. Key Goal: To optimize processes to deliver maximum customer value at the lowest possible cost. Components: Plan, Source, Make, Deliver, Return, Enable. 2. Supply Chain Drivers Facilities: Locations where inventory is stored, assembled, or fabricated (e.g., production sites, warehouses). Inventory: Raw materials, WIP (Work-in-Process), finished goods within the supply chain. Transportation: Moving inventory from point to point in the supply chain (e.g., air, truck, rail, sea). Information: Data and analysis regarding facilities, inventory, transportation, costs, prices, and customers. Sourcing: Deciding who will perform a particular supply chain activity. Pricing: How much a firm will charge for the goods and services it provides. 3. Supply Chain Strategy Alignment: Matching supply chain capabilities with competitive strategy. Competitive Strategy: Defines the set of customer needs a firm seeks to satisfy through its products and services. Supply Chain Strategy: Determines the nature of procurement, transportation of materials, manufacture of product, and distribution of product. Strategic Fit: Consistency between customer priorities of competitive strategy and supply chain capabilities specified by the supply chain strategy. Efficiency vs. Responsiveness: Efficient SC: Focus on cost reduction, economies of scale, high utilization. Best for functional products (predictable demand). Responsive SC: Focus on speed, flexibility, ability to meet diverse customer needs. Best for innovative products (unpredictable demand). 4. Demand Forecasting Importance: Basis for all strategic and operational plans in a supply chain. Types of Forecasts: Qualitative: Market research, expert opinion, Delphi method. Quantitative: Time Series: Moving average, exponential smoothing, trend projection. Causal: Regression analysis (e.g., demand as a function of price). Forecast Error: Mean Absolute Deviation (MAD): $MAD = \frac{\sum |Actual - Forecast|}{n}$ Mean Squared Error (MSE): $MSE = \frac{\sum (Actual - Forecast)^2}{n}$ Mean Absolute Percentage Error (MAPE): $MAPE = \frac{\sum \frac{|Actual - Forecast|}{Actual}}{n} \times 100\%$ 5. Inventory Management Purpose: To buffer against uncertainty, achieve economies of scale, and support customer service. Costs: Holding costs, ordering costs, shortage costs. Economic Order Quantity (EOQ): Optimal order quantity that minimizes total holding and ordering costs. $$ EOQ = \sqrt{\frac{2DS}{H}} $$ Where: $D$ = Annual Demand, $S$ = Ordering Cost per order, $H$ = Holding Cost per unit per year. Reorder Point (ROP): Level of inventory at which a new order should be placed. $$ ROP = (\text{Demand per day} \times \text{Lead time in days}) + \text{Safety Stock} $$ Safety Stock: Inventory held to guard against uncertainty in demand or lead time. ABC Analysis: Categorizing inventory items based on their value (A: high value, C: low value). 6. Transportation Management Modes: Rail: High capacity, low cost, slow. Truck: Flexible, moderate speed, moderate cost. Air: Fast, high cost, low capacity. Water: Very high capacity, very low cost, very slow. Pipeline: High capacity, low operating cost, limited to liquids/gases. Intermodal Transportation: Using multiple modes for a single shipment (e.g., rail-truck). Key Decisions: Mode selection, carrier selection, route optimization, shipment consolidation. 7. Facility Location & Network Design Factors: Proximity to customers, suppliers, labor costs, infrastructure, taxes, regulations. Network Design Decisions: Number, location, and size of facilities. Assignment of facilities to markets. Allocation of capacity to facilities. Methods: Centroid Method: Locates a single facility to minimize transportation costs based on volume and coordinates. $$ C_x = \frac{\sum D_i x_i}{\sum D_i}, \quad C_y = \frac{\sum D_i y_i}{\sum D_i} $$ Where $D_i$ = volume at location $i$, $(x_i, y_i)$ = coordinates of location $i$. Gravity models. Optimization models (linear programming). 8. Supply Chain Relationships & Collaboration Supplier Relationship Management (SRM): Managing interactions with organizations that supply goods and/or services. Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Managing interactions with current and potential customers. Partnerships: Strategic alliances, joint ventures, vendor-managed inventory (VMI). Bullwhip Effect: Demand variability increases upstream in the supply chain. Causes: Demand forecast updating, order batching, price fluctuations, rationing/gaming. Mitigation: Information sharing, VMI, everyday low pricing (EDLP), lead time reduction. 9. Global Supply Chains Challenges: Increased lead times, higher transportation costs, exchange rate fluctuations, political instability, cultural differences, tariffs, customs regulations. Opportunities: Access to new markets, lower labor costs, access to specialized skills/resources. Risk Management: Identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks (e.g., supply disruptions, quality issues, geopolitical events). 10. Sustainable Supply Chains Triple Bottom Line: People, Planet, Profit. Environmental Considerations: Reducing carbon footprint, waste reduction, sustainable sourcing, reverse logistics. Social Considerations: Ethical labor practices, fair wages, safety, community engagement. Circular Economy: Moving from a linear "take-make-dispose" model to one that emphasizes reuse, repair, and recycling. 11. Supply Chain Technologies Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP): Integrated software system managing core business processes. Warehouse Management Systems (WMS): Manages operations within a warehouse. Transportation Management Systems (TMS): Optimizes transportation planning and execution. Advanced Planning and Scheduling (APS): Optimizes production and distribution plans. Blockchain: Distributed ledger technology for secure and transparent transactions. Internet of Things (IoT): Network of physical objects embedded with sensors to collect and exchange data. Artificial Intelligence (AI) & Machine Learning (ML): For demand forecasting, optimization, automation.