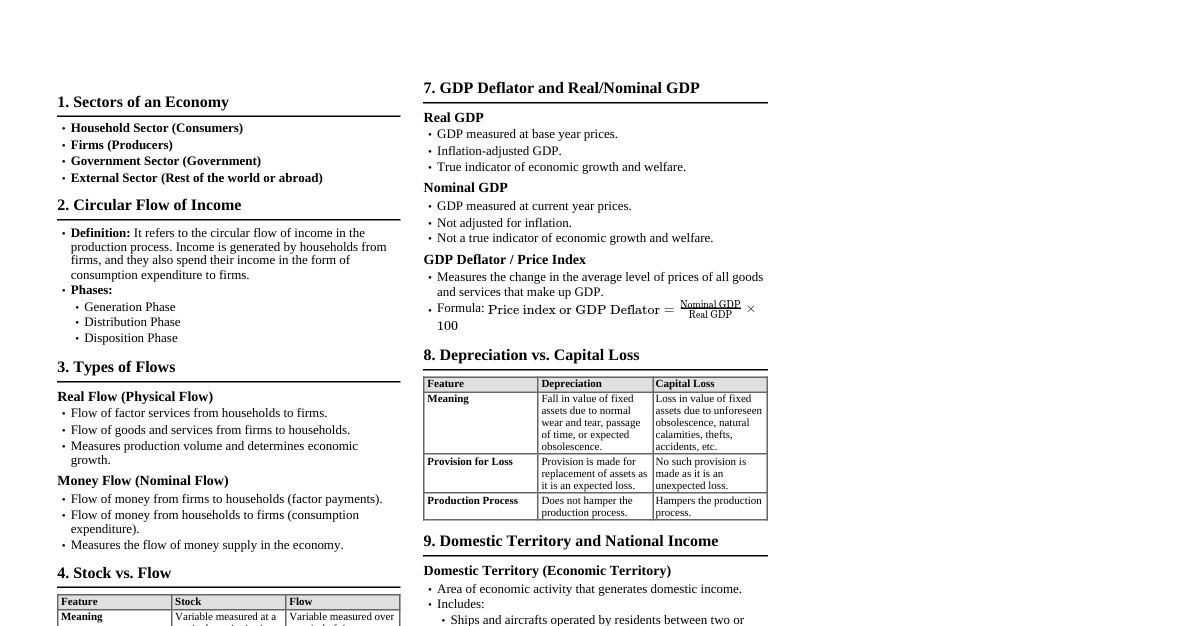
I. Compensation Income Income arising from an employer-employee relationship. A. Employer-Employee Relationship Elements (Case Law) Selection and engagement of employees: Screening process for hiring. Payment of wages: Employer fixes and controls wage payment. Power of dismissal: Employer can retrench or terminate. Power of control: Employer controls means and methods of work. An arrangement not meeting all elements is an independent contract, not employer-employee. B. Not Considered Employees Consultants Directors without management function Talents/artists on TV/radio (e.g., Sonza vs. ABS-CBN ) Income for these individuals is business or professional income, not compensation. C. Types of Employees (Function) Managerial employees: Lay down/execute policies, hire/fire, discipline. Supervisory employees: Effectively recommend managerial actions requiring independent judgment. Rank and file employees: Neither managerial nor supervisory functions. D. Types of Employees (Taxability) Minimum Wage Earners (MWE): Exempt from income tax on compensation. Regular employees: Subject to regular progressive income tax. A minimum wage earner is a worker paid the statutory minimum wage (fixed by RTWPB or P5,000/month, P60,000/year, whichever is higher). E. Tax Model on Compensation Income Description Amount Gross compensation income P XXX,XXX Less: Non-taxable compensation XXX,XXX Taxable compensation income P XXX,XXX F. Gross Compensation Income Includes all remunerations received under an employer-employee relationship. G. Non-Taxable Compensation Mandatory Deductions: GSIS, SSS, PhilHealth, HDMF, union dues. Exempt Benefits: Excluded/exempted under NIRC & special laws. Exempt under treaty/international agreements. Necessary for trade/business/profession of employer. For convenience or advantage of employer. H. Exempt Benefits under NIRC, as amended, and Special Laws Remunerations received as incidents of employment: Exempt retirement benefits (RA 7641), including government retirement gratuities. Exempt termination benefits. Benefits from US Veterans Administration. Social security, retirement gratuities, pensions from foreign government agencies/institutions. Benefits from SSS (SSS Act of 1954). Benefits from GSIS (GSIS Act of 1937). COVID-19 benefits for health workers (RA 11494 BAYANIHAN 2): Special Risk Allowance, Actual Hazard Duty Pay, Compensation for COVID-19 contracted in line of duty. De minimis benefits: Facilities/privileges of relatively small value, promoting health, goodwill, contentment, or efficiency. Exempt from income tax. 13th month pay and other benefits: Not exceeding P90,000. Certain benefits of minimum wage earners. I. De Minimis Benefits (RR5-2011, as amended by RR 11-2018) Monetized unused vacation leave credits (private employees) not exceeding 10 days. Monetized unused vacation and sick leave credits (government employees). Medical cash allowance to dependents not exceeding P1,500/semester or P250/month. Rice subsidy not exceeding P2,000 or 1 sack of 50-kg rice/month. Uniform and clothing allowance not exceeding P6,000/annum. Actual Medical Assistance (e.g., check-up, maternity) not exceeding P10,000/annum. Laundry allowance not exceeding P300/month. Employee achievement awards (tangible property, not cash/gift certificates) with annual monetary value not exceeding P10,000. Gifts during Christmas & major anniversary celebrations not exceeding P5,000/employee/annum. Daily meal allowance for overtime/night shift not exceeding 25% of basic minimum wage. Benefits from CBA and productivity incentive schemes not exceeding P10,000/employee/taxable year. J. Taxable De Minimis Benefits Excess de minimis over regulatory limits. Other benefits of relatively small value not included in the list above. Treatment: Rank and file employees: Treated as "other compensation income" under "13th month pay and other benefits." Managerial and supervisory employees: Treated as fringe benefit subject to final fringe benefit tax. K. Composition of Taxable Compensation Income Regular compensation: Fixed remunerations received every payroll period (basic salary, fixed allowances like COLA, housing, representation, transportation). Supplemental compensation: Performance-based pays (overtime, hazard, night shift differential, holiday pay, commissions, director's fees (if employee), emoluments/honoraria, taxable retirement/separation pay, value of living quarters/meals, gains on stock options, profit sharing, taxable bonuses). 13th Month Pay and Other Benefits: Incentive pays and other taxable employee benefits not classifiable as regular/supplemental compensation. Excluded from gross income up to P90,000; excess is added to supplemental compensation. L. Fixed Allowances Fixed allowances regularly received are part of regular compensation. Exception: ordinary and necessary allowances for travel, representation, or entertainment, subject to accounting, where excess advances are returned to employer. Variable and liquidated allowances are not taxed unless retained by employee. M. Non-Compensation Items Fees: Retainer fees of consultants, talents, directors without management function are professional income. Commissions: To non-employees (e.g., independent sales agents) are business income. Tips and gratuities: Paid directly by customers, not accounted for to employer, are "other income" in income tax return. N. Tax Treatment of 13th Month Pay and Other Benefits Exempt from withholding on compensation up to P90,000. Excess over P90,000 is subject to withholding tax on compensation (RR2-98). RR3-98 states fringe benefit tax does not cover benefits part of compensation income subject to withholding tax. II. Income Tax Computations A. Problem 1: AA - Professional Income Advances for future services rendered: P50,000 Cash collections for services rendered during taxable year: P30,000 Collection from clients for services rendered last taxable year: P20,000 Taxable Gross Income: P30,000 (only services rendered and collected in the current year are taxable for cash basis practitioners). B. Problem 2: BB - Various Income Sources Dividend from Domestic Corporation: P100,000 (Exempt) Dividend from Foreign Corporation: P50,000 (Taxable) Share of Net Income from Business partnership: P100,000 (Taxable) Share of Net Income from Professional Partnership: P300,000 (Taxable) Received prizes from PCSO: P10,000 (Exempt under special laws) Income received from share of undivided estate: P20,000 (Taxable) Total Taxable Gross Income: $50,000 + 100,000 + 300,000 + 20,000 = \text{P}470,000$ C. Problem 3: CC - Income Tax Payable (TRAIN Law) Compensation Income from employment: P450,000 Income from the conduct of business: P850,000 Other Income subject to regular tax: P350,000 Creditable withholding tax (BIR form 2307): P5,000 Total Taxable Income: $450,000 + 850,000 + 350,000 = \text{P}1,650,000$ Tax Computation using TRAIN Law (Year 2023 Onwards): Taxable Income: P1,650,000 Applicable Bracket: Above P800,000 to P2,000,000 Tax Rate: P102,500 + 25% of excess over P800,000 Excess over P800,000: $1,650,000 - 800,000 = \text{P}850,000$ Tax on P850,000: $850,000 \times 0.25 = \text{P}212,500$ Total Income Tax Due: $102,500 + 212,500 = \text{P}315,000$ Less: Creditable Withholding Tax: P5,000 Tax Payable: $315,000 - 5,000 = \text{P}310,000$ III. Illustrations for Compensation Income Components A. Illustration 1: Taxable De Minimis Benefits (Alexanderia) Benefit Actual Limit Excess (Taxable) Monetized unused VL P 5,400 P 6,000 P 0 Monetized unused SL 5,400 0 5,400 Medical assistance 7,000 10,000 0 Rice subsidy 30,000 24,000 6,000 Clothing allowance 9,000 6,000 3,000 Laundry allowance 6,000 3,600 2,400 Taxable de minimis as "other benefits" P 16,800 B. Illustration 2: Taxable Compensation Income (Employee Termination) Unpaid 2021 salaries: P200,000 Unpaid 2020 salaries: P20,000 Reimbursement for transportation expenses: P10,000 (Non-taxable if liquidated) Termination pay: P100,000 (Exempt if due to business closure and not fault of employee) Gross Compensation Income: $200,000 + 20,000 + 10,000 + 100,000 = \text{P}330,000$ Less: Non-taxable compensation Non-taxable benefits (Termination Pay): P100,000 Taxable Compensation Income: $330,000 - 100,000 = \text{P}230,000$ C. Illustration 3: Taxable 13th Month Pay and Other Benefits (Government Employee) Benefits received: Christmas bonus: P70,000 Cash gift: P5,000 Additional compensation allowance: P36,000 Personnel Economic Relief Allowance (P2,000/month): P24,000 Monetized value of vacation leave and sick leave (18 days): P9,000 Uniform and clothing allowance: P7,000 Solution: Christmas bonus (13th month pay): P70,000 Cash gift: P5,000 Additional compensation allowance: P36,000 Excess uniform and clothing allowance ($P7,000 - P6,000$ limit): P1,000 Total 13th month pay and other benefits: $70,000 + 5,000 + 36,000 + 1,000 = \text{P}112,000$ Less: Exclusion Threshold: P90,000 Taxable 13th month pay and other benefits: $112,000 - 90,000 = \text{P}22,000$ D. Illustration 4: Taxable 13th Month Pay and Other Benefits (Private Employee) Benefits received: 13th month pay: P72,000 Performance bonus: P15,000 Christmas gift: P30,000 Danger exposure allowance (hazard pay): P6,000 Housing privilege: P38,000 Uniform and clothing allowance: P8,000 Laundry allowance: P6,000 Solution: Benefit De Minimis Limit Other Benefits (Taxable) Christmas gift P 30,000 P 5,000 P 25,000 Uniform and clothing allowance 8,000 6,000 2,000 Laundry allowance 6,000 3,600 2,400 Excess de minimis benefits (other fringe benefits) P 29,400 13th month pay: P72,000 Total 13th month pay and other benefits: $72,000 + 29,400 = \text{P}101,400$ Less: Exclusion threshold: P90,000 Taxable 13th month pay and other benefits: $101,400 - 90,000 = \text{P}11,400$ E. Illustration 5: Managerial Employee Benefits Benefits received: 13th month pay: P95,000 Rental expense on condominium unit: P18,000 Salary of personal bodyguard: P12,000 Profit sharing: P12,000 Rice allowance: P32,400 Clothing allowance: P7,000 Night shift differential pay: P11,000 Solution: Benefit De Minimis Limit Other Benefits (Taxable) Rice allowance P 32,400 P 24,000 P 8,400 Clothing allowance 7,000 6,000 1,000 Excess de minimis P 9,400 Other fringe benefits (subject to fringe benefit tax): Rent of residence paid by employer: P18,000 Salary of personal bodyguard: P12,000 Total fringe benefit subject to fringe benefit tax: $18,000 + 12,000 = \text{P}30,000$ Additional Compensation: Profit sharing: P12,000 Night shift differential pay: P11,000 Total supplemental compensation: $12,000 + 11,000 = \text{P}23,000$ Taxable 13th month pay and other benefits: Total 13th month pay and other benefits (P95,000 + P9,400): P104,400 Less: Exclusion threshold: P90,000 Taxable 13th month pay and other benefits: $104,400 - 90,000 = \text{P}14,400$ F. Illustration 6: Minimum Wage Earner (MWE) Taxability Ms. Guevarra, MWE, received: Basic minimum wage: P124,000 13th month pay: P11,000 Overtime pay: P80,000 Night shift differential pay: P30,000 Hazard pay: P15,000 Holiday pay: P15,000 Less: SSS, PhilHealth, HDMF contributions: P5,000 Taxable Compensation Income: P0 (MWE are exempt from income tax on basic minimum wage and other benefits like HHON - Holiday pay, Hazard pay, Overtime pay, Night shift differential pay, and mandatory contributions). G. Illustration 7: MWE with Other Taxable Compensation Income Mary Dela Fuente, MWE, received: Basic minimum wage, net of P8,000 mandatory deductions: P160,800 13th month pay: P14,000 Holiday pay: P4,000 Overtime pay: P70,000 Night shift differential pay: P15,000 Hazard pay: P10,000 Profit sharing bonus: P12,000 Commission income: P370,000 Gross Compensation Income: P160,800 (Basic MW) + P8,000 (Mandatory Deductions) + P14,000 (13th month pay) + P4,000 (Holiday pay) + P70,000 (Overtime pay) + P15,000 (Night shift differential pay) + P10,000 (Hazard pay) + P12,000 (Profit sharing bonus) + P370,000 (Commission income) = P663,800 Less: Non-taxable compensation income Mandatory deductions: P8,000 Exempt benefits (Basic MW + HHON + 13th month pay up to P90k): P160,800 + P14,000 + P4,000 + P70,000 + P15,000 + P10,000 = P273,800 Total Non-taxable Compensation: $8,000 + 273,800 = \text{P}281,800$ Taxable Compensation Income: $663,800 - 281,800 = \text{P}382,000$ Tax Due Computation: Taxable Compensation Income: P382,000 Lower limit of income bracket (P250,000 and below): P250,000 (Tax = P0) Excess: $382,000 - 250,000 = \text{P}132,000$ Multiply by (Rate for P250,000 to P400,000): 20% Tax on Excess: $132,000 \times 0.20 = \text{P}26,400$ Total Tax Due: P26,400