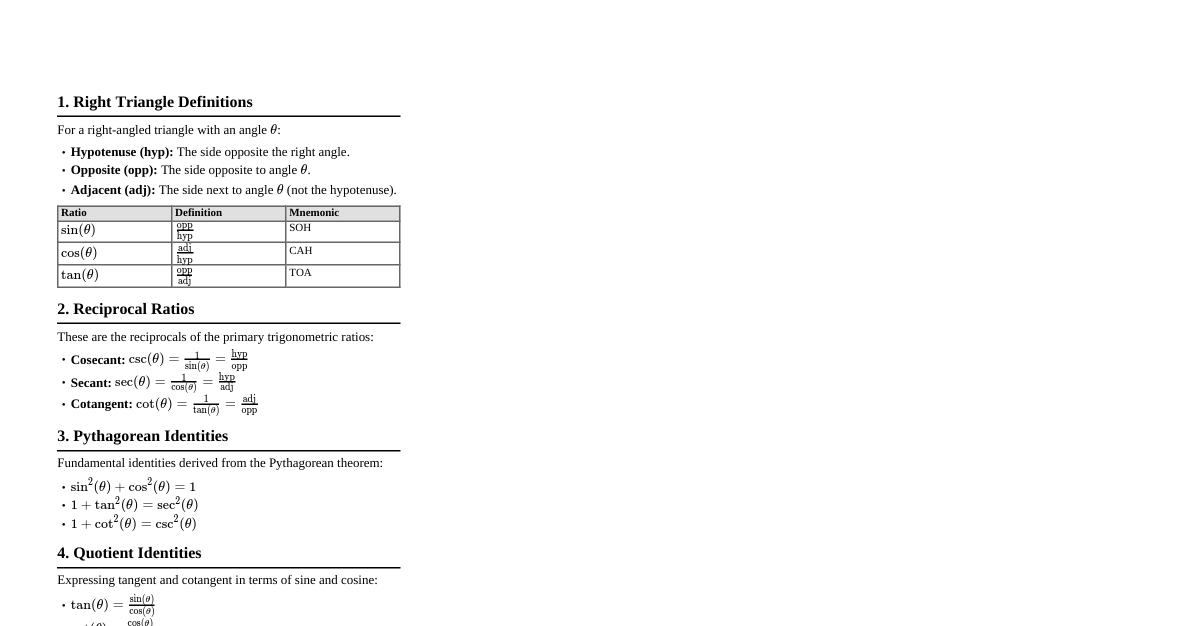
### Unit Circle: Basics - **Definition:** A circle with radius 1 centered at the origin (0,0) in the Cartesian coordinate system. - **Coordinates:** For any point $(x,y)$ on the unit circle, $x = \cos\theta$ and $y = \sin\theta$, where $\theta$ is the angle from the positive x-axis. - **Equation:** $x^2 + y^2 = 1$ - **Angles:** Measured counter-clockwise from the positive x-axis. - Positive angles: Counter-clockwise - Negative angles: Clockwise - **Radians vs. Degrees:** - $2\pi$ radians = $360^\circ$ - $\pi$ radians = $180^\circ$ - To convert degrees to radians: Angle (degrees) $\times \frac{\pi}{180^\circ}$ - To convert radians to degrees: Angle (radians) $\times \frac{180^\circ}{\pi}$ ### Unit Circle: Key Values | Degrees | Radians | $\cos\theta$ | $\sin\theta$ | $\tan\theta$ | | :------ | :--------------- | :--------------------- | :--------------------- | :--------------------- | | $0^\circ$ | $0$ | $1$ | $0$ | $0$ | | $30^\circ$ | $\pi/6$ | $\sqrt{3}/2$ | $1/2$ | $1/\sqrt{3}$ or $\sqrt{3}/3$ | | $45^\circ$ | $\pi/4$ | $\sqrt{2}/2$ | $\sqrt{2}/2$ | $1$ | | $60^\circ$ | $\pi/3$ | $1/2$ | $\sqrt{3}/2$ | $\sqrt{3}$ | | $90^\circ$ | $\pi/2$ | $0$ | $1$ | Undefined | | $180^\circ$ | $\pi$ | $-1$ | $0$ | $0$ | | $270^\circ$ | $3\pi/2$ | $0$ | $-1$ | Undefined | | $360^\circ$ | $2\pi$ | $1$ | $0$ | $0$ | #### Quadrant Signs - **Quadrant I (0 to $\pi/2$):** $\cos(+)$, $\sin(+)$, $\tan(+)$ - **Quadrant II ($\pi/2$ to $\pi$):** $\cos(-)$, $\sin(+)$, $\tan(-)$ - **Quadrant III ($\pi$ to $3\pi/2$):** $\cos(-)$, $\sin(-)$, $\tan(+)$ - **Quadrant IV ($3\pi/2$ to $2\pi$):** $\cos(+)$, $\sin(-)$, $\tan(-)$ ### Fundamental Identities - **Reciprocal Identities:** - $\csc\theta = \frac{1}{\sin\theta}$ - $\sec\theta = \frac{1}{\cos\theta}$ - $\cot\theta = \frac{1}{\tan\theta}$ - **Quotient Identities:** - $\tan\theta = \frac{\sin\theta}{\cos\theta}$ - $\cot\theta = \frac{\cos\theta}{\sin\theta}$ - **Pythagorean Identities:** - $\sin^2\theta + \cos^2\theta = 1$ - $1 + \tan^2\theta = \sec^2\theta$ - $1 + \cot^2\theta = \csc^2\theta$ ### Co-function Identities - $\sin(\pi/2 - \theta) = \cos\theta$ - $\cos(\pi/2 - \theta) = \sin\theta$ - $\tan(\pi/2 - \theta) = \cot\theta$ - $\csc(\pi/2 - \theta) = \sec\theta$ - $\sec(\pi/2 - \theta) = \csc\theta$ - $\cot(\pi/2 - \theta) = \tan\theta$ ### Even/Odd Identities - **Even Functions:** $\cos(-\theta) = \cos\theta$, $\sec(-\theta) = \sec\theta$ - **Odd Functions:** - $\sin(-\theta) = -\sin\theta$ - $\tan(-\theta) = -\tan\theta$ - $\csc(-\theta) = -\csc\theta$ - $\cot(-\theta) = -\cot\theta$ ### Sum and Difference Identities - $\sin(A \pm B) = \sin A \cos B \pm \cos A \sin B$ - $\cos(A \pm B) = \cos A \cos B \mp \sin A \sin B$ - $\tan(A \pm B) = \frac{\tan A \pm \tan B}{1 \mp \tan A \tan B}$ ### Double-Angle Identities - $\sin(2\theta) = 2\sin\theta\cos\theta$ - $\cos(2\theta) = \cos^2\theta - \sin^2\theta$ - $= 2\cos^2\theta - 1$ - $= 1 - 2\sin^2\theta$ - $\tan(2\theta) = \frac{2\tan\theta}{1 - \tan^2\theta}$ ### Half-Angle Identities - $\sin(\theta/2) = \pm\sqrt{\frac{1 - \cos\theta}{2}}$ - $\cos(\theta/2) = \pm\sqrt{\frac{1 + \cos\theta}{2}}$ - $\tan(\theta/2) = \pm\sqrt{\frac{1 - \cos\theta}{1 + \cos\theta}} = \frac{1 - \cos\theta}{\sin\theta} = \frac{\sin\theta}{1 + \cos\theta}$ *The sign depends on the quadrant of $\theta/2$.* ### Power-Reducing Identities - $\sin^2\theta = \frac{1 - \cos(2\theta)}{2}$ - $\cos^2\theta = \frac{1 + \cos(2\theta)}{2}$ - $\tan^2\theta = \frac{1 - \cos(2\theta)}{1 + \cos(2\theta)}$ ### Product-to-Sum Identities - $\sin A \cos B = \frac{1}{2}[\sin(A+B) + \sin(A-B)]$ - $\cos A \sin B = \frac{1}{2}[\sin(A+B) - \sin(A-B)]$ - $\cos A \cos B = \frac{1}{2}[\cos(A+B) + \cos(A-B)]$ - $\sin A \sin B = \frac{1}{2}[\cos(A-B) - \cos(A+B)]$ ### Sum-to-Product Identities - $\sin A + \sin B = 2\sin\left(\frac{A+B}{2}\right)\cos\left(\frac{A-B}{2}\right)$ - $\sin A - \sin B = 2\cos\left(\frac{A+B}{2}\right)\sin\left(\frac{A-B}{2}\right)$ - $\cos A + \cos B = 2\cos\left(\frac{A+B}{2}\right)\cos\left(\frac{A-B}{2}\right)$ - $\cos A - \cos B = -2\sin\left(\frac{A+B}{2}\right)\sin\left(\frac{A-B}{2}\right)$ ### Inverse Trigonometric Functions - $\arcsin x = \theta \iff \sin\theta = x$, where $-\pi/2 \le \theta \le \pi/2$ - $\arccos x = \theta \iff \cos\theta = x$, where $0 \le \theta \le \pi$ - $\arctan x = \theta \iff \tan\theta = x$, where $-\pi/2 ### Graph Characteristics - **Sine Function:** - Period: $2\pi$ - Domain: $(-\infty, \infty)$ - Range: $[-1, 1]$ - Odd function (symmetric about the origin) - **Cosine Function:** - Period: $2\pi$ - Domain: $(-\infty, \infty)$ - Range: $[-1, 1]$ - Even function (symmetric about the y-axis) - **Tangent Function:** - Period: $\pi$ - Domain: $x \ne \pi/2 + n\pi$ for integer $n$ - Range: $(-\infty, \infty)$ - Odd function (symmetric about the origin) - **General Form:** $y = A \sin(Bx - C) + D$ or $y = A \cos(Bx - C) + D$ - $|A|$ = Amplitude - Period = $2\pi/|B|$ - Phase Shift = $C/B$ (to the right if $C/B > 0$, to the left if $C/B 0$, down if $D