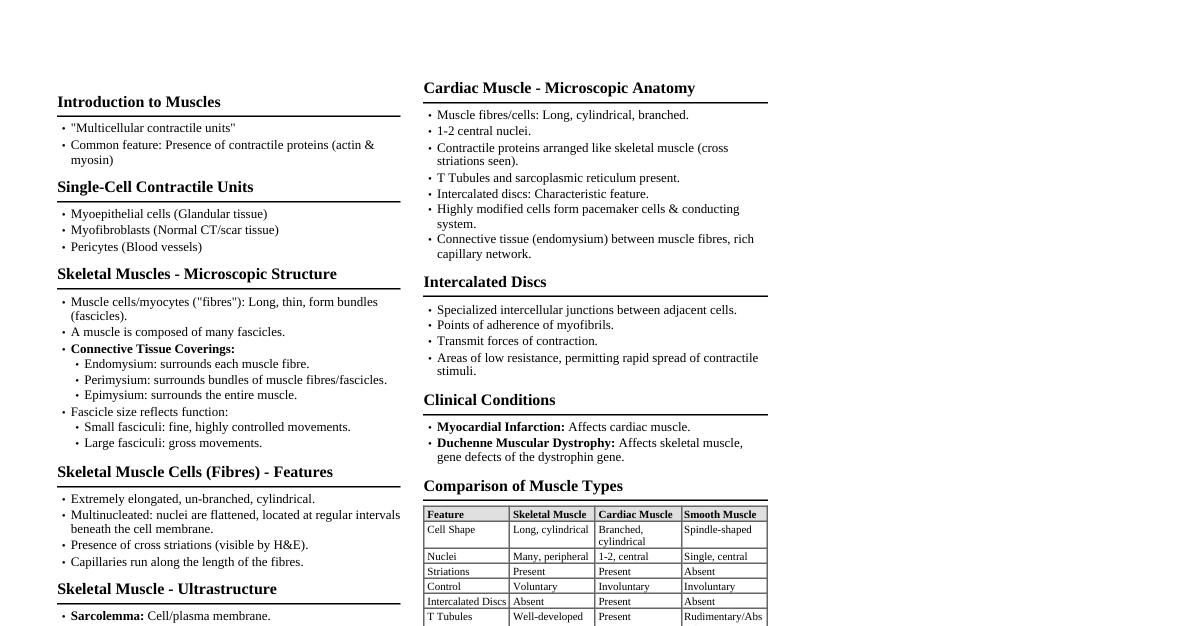
I. Overview of Facial Nerve (CN VII) Type: Mixed nerve (motor, sensory, parasympathetic) Origin: Pons (brainstem) Exit from Skull: Internal acoustic meatus, then facial canal, exits via stylomastoid foramen. Main Functions: Motor: Muscles of facial expression, stapedius, posterior belly of digastric, stylohyoid. Sensory: Taste from anterior 2/3 of tongue, sensation from external ear and small area behind ear. Parasympathetic: Lacrimal gland, submandibular and sublingual salivary glands. II. Course and Branches A. Intracranial Course Emerges from pontomedullary junction. Enters internal acoustic meatus with vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII). Traverses facial canal in petrous part of temporal bone. Forms geniculate ganglion (sensory ganglion). B. Intratemporal Branches (within facial canal) Greater Petrosal Nerve: Origin: Geniculate ganglion. Function: Parasympathetic to lacrimal gland, nasal and palatine glands (via pterygopalatine ganglion). Nerve to Stapedius: Function: Motor to stapedius muscle (dampens sound). Chorda Tympani: Origin: Just before stylomastoid foramen. Function: Taste from anterior 2/3 of tongue. Parasympathetic to submandibular and sublingual glands (via submandibular ganglion). C. Extracranial Branches (after exiting stylomastoid foramen) Posterior Auricular Nerve: Motor to occipitalis, posterior and superior auricular muscles. Branches to Digastric (posterior belly) and Stylohyoid muscles. Terminal Motor Branches (within parotid gland, forming plexus): T emporal: Orbicularis oculi, frontalis. Z ygomatic: Orbicularis oculi, zygomaticus major/minor. B uccal: Orbicularis oris, buccinator. M arginal Mandibular: Depressor anguli oris, mentalis. C ervical: Platysma. Mnemonic: "To Zanzibar By Motor Car" III. Functional Components Special Visceral Efferent (SVE): Motor to muscles of facial expression, stapedius, posterior belly of digastric, stylohyoid. General Visceral Efferent (GVE): Parasympathetic to lacrimal, submandibular, sublingual glands. Special Visceral Afferent (SVA): Taste from anterior 2/3 of tongue. General Somatic Afferent (GSA): Sensation from concha of external ear, retroauricular skin. IV. Clinical Significance A. Facial Nerve Palsy (Bell's Palsy) Definition: Idiopathic, acute onset unilateral facial paralysis. Cause: Often viral (e.g., Herpes Simplex) leading to inflammation and compression of nerve in facial canal. Symptoms: Inability to wrinkle forehead. Drooping eyebrow. Inability to close eye on affected side (lagophthalmos). Drooping corner of mouth. Difficulty with speech and eating. Loss of taste (anterior 2/3 tongue). Hyperacusis (due to stapedius paralysis). Decreased lacrimation/salivation (less common). Distinction from Stroke: Bell's Palsy (LMN lesion): Affects entire ipsilateral face, including forehead. Stroke (UMN lesion): Spares forehead (due to bilateral cortical innervation of upper face muscles). B. Other Lesions Ramsay Hunt Syndrome: Caused by Varicella-Zoster virus reactivation in geniculate ganglion. Presents with facial palsy, painful vesicular rash in external ear canal/auricle, and sometimes hearing loss/vertigo. Acoustic Neuroma: Tumor of CN VIII in cerebellopontine angle, can compress CN VII, leading to facial weakness. Parotid Gland Tumors: Facial nerve passes through parotid gland; tumors can compress or invade nerve, causing palsy. C. Tests Motor: Ask patient to wrinkle forehead, close eyes tightly, smile, puff cheeks. Taste: Apply sweet, sour, salty, bitter solutions to anterior 2/3 of tongue. Lacrimation: Schirmer test (less common for routine exam). V. Diagram of Facial Nerve Branches Brainstem (Pons) CN VII Origin IAM Geniculate Ganglion Stylomastoid Foramen Greater Petrosal N. Lacrimal Gland N. to Stapedius Stapedius M. Chorda Tympani Submandibular/Lingual Glands Ant. 2/3 Tongue (Taste) Posterior Auricular N. To Digastric/Stylohyoid Terminal Branches (Parotid Plexus) Temporal (Frontalis, Orb. Oculi) Zygomatic (Orb. Oculi, Zygomaticus) Buccal (Buccinator, Orb. Oris) Marginal Mandibular (Depressor Anguli Oris) Cervical (Platysma)